Field help
Residence in Germany
Specify the period in which you were resident in Germany in 2022.
Please only provide information here if you moved to Germany or moved abroad during the course of 2022.
If you had your residence partially in Germany and partially abroad during the tax year, you were not fully taxable in Germany for the entire year. For the period that you lived in Germany, you are a fully taxable person.
The foreign income received beyond this period and which is not liable to German income tax is taken into account in the calculation of income tax (so-called "progression clause" (Progressionsvorbehalt)).
Foreign income
Enter the total amount of foreign income that is not subject to German income tax. The income to be declared is the income received minus the expenses claimed.
Example: You have earned income abroad as an employee from January to July 2022. To determine the foreign income, you should deduct the foreign income-related expenses actually incurred in full from the foreign income (here: the foreign gross income).
Under German tax law, foreign income is only taken into account when calculating the tax rate that is applied to your taxable German income (progression clause).
The foreign income must be determined in accordance with German tax law. In accordance with section 34d of the Income Tax Act (EStG), the total foreign income is comprised of:
- Income from agriculture and forestry carried on in a foreign state,
- Income from commercial business abroad,
- Income from self-employment carried out abroad,
- Income from the sale of assets abroad,
- Income from employment abroad,
- Income from capital assets if the debtor has a residence, management or registered office abroad or if the capital assets are secured by foreign real estate,
- Income from renting and leasing abroad and
- Other income earned abroad.
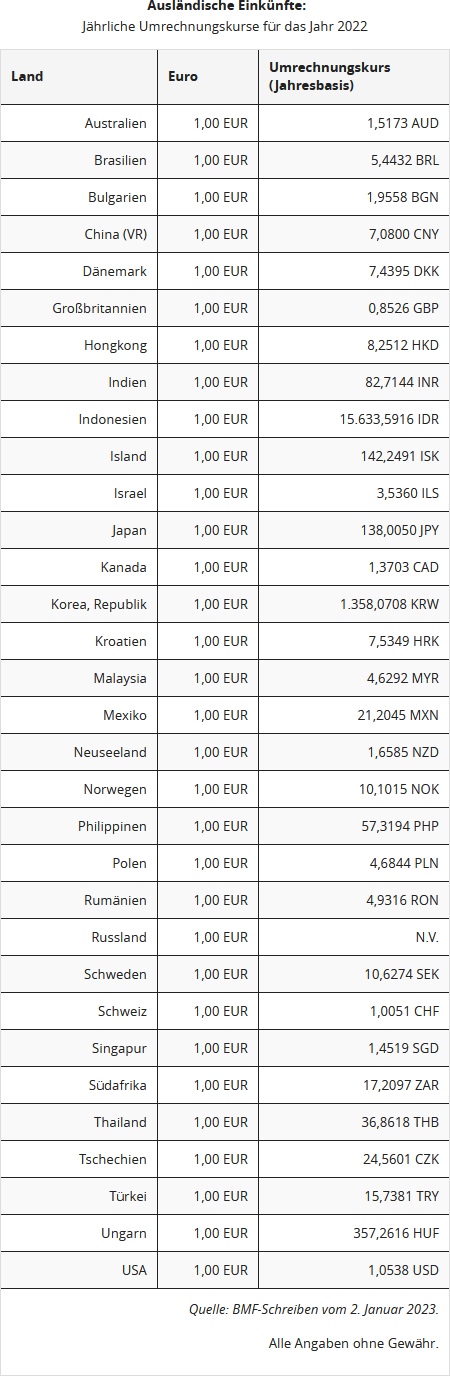
The conversion of income in foreign currency must be done on a monthly basis using the European Central Bank's euro reference rate. However, it is not objectionable if wage payments received in a foreign currency are converted on the basis of an annual conversion rate - determined from the monthly published VAT reference rates, rounded down to the nearest 50 cents. (Ministry of Finance (BMF) letter dated Dec. 14, 2014)
Here is an overview of the annual conversion rates for the key foreign currencies.
Foreign income
Enter the total amount of foreign income that is not subject to German income tax. If you did not have any foreign income, enter "0" here.
If applying for unlimited tax liability or applying for the personal and family-related tax benefits, the amount of foreign income earned during the time abroad which was not subject to German income tax must be checked.
This income is taken into account when determining your tax rate (so-called "progression clause (Progressionsvorbehalt)". This means that the income is used as the basis for stipulating the rate of tax you need to pay on your taxable income.
The conversion of income in foreign currency must be done on a monthly basis using the Euro reference rate from the European Central Bank. However, it is not objectionable if wage payments received in a foreign currency are converted on the basis of an annual conversion rate - determined from the VAT reference rates published monthly, rounded down to the nearest 50 cents. (Ministry of Finance (BMF) letter dated 14.12.2014)
Here is an overview of the annual conversion rates for the key foreign currencies.
Did Partner A hold a share in a corporation?
Specify whether you invested in a corporation or cooperative within the meaning of section 17 of the Income Tax Act (EStG) in 2022.
Please enter the information here only if you moved to Germany or moved away from Germany in 2022.
... foreign investment income included therein
Specify the foreign capital gains which are subject to withholding tax or which would be subject to withholding tax in Germany.
If applying for unlimited tax liability or applying for the personal and family-related tax benefits, the amount of foreign income earned during the time abroad which was not subject to German income tax must be checked.
The conversion of income in foreign currency must be done on a monthly basis using the Euro reference rate of the European Central Bank. However, it is not objectionable if wage payments received in a foreign currency are converted on the basis of an annual conversion rate - determined from the VAT reference rates published monthly, rounded down to the nearest 50 cents. (Ministry of Finance (BMF) letter dated 14.12. 2014)
Here is an overview of the annual conversion rates for the key foreign currencies.
... extraordinary income included therein
Specify the total extraordinary income that is not subject to German income tax.
Extraordinary income includes in particular:
- Remuneration for activities lasting several years
- Capital gains
- Compensations within the meaning of § 24 No. 1 Income Tax Act (EStG)
If applying for unlimited tax liability or applying for the personal and family-related tax benefits, the amount of foreign income earned during the time abroad which was not subject to German income tax must be checked.
Extraordinary income must be taken into account when determining the tax rate, (so-called "progression clause (Progressionsvorbehalt)"). This means that the income is included at the rate of one-fifth when determining your tax rate but not when determining your taxable income.
The conversion of income in foreign currency must be done on a monthly basis using the Euro reference rate from the European Central Bank. However, it is not objectionable if wage payments received in a foreign currency are converted on the basis of an annual conversion rate - determined from the VAT reference rates published monthly, rounded down to the nearest 50 cents. (Ministry of Finance (BMF) letter dated 14.12.2014)
Here is an overview of the annual conversion rates for the key foreign currencies.
... extraordinary income included therein
Specify the extraordinary income according to sections 34 and 34 b Income Tax Act (EStG). This must be income which is not subject to German income tax.
Extraordinary income includes in particular:
- Remuneration for activities lasting several years
- Capital gains
- Compensations within the meaning of sect. 24 No. 1 Income Tax Act (EStG)
Extraordinary income must be taken into account when determining the tax rate, (so-called "German progression clause (Progressionsvorbehalt)"). This means that the income is included at the rate of one-fifth when determining your tax rate but not when determining your taxable income.
The conversion of income in foreign currency must be done on a monthly basis using the European Central Bank's euro reference rate. However, it is not objectionable if wage payments received in a foreign currency are converted on the basis of an annual conversion rate - determined from the monthly published VAT reference rates, rounded down to the nearest 50 cents. (Ministry of Finance (BMF) letter dated Dec. 14, 2014)
Here is an overview of the annual conversion rates for the key foreign currencies.
Did Partner A reside at least temporarily in a low-tax country?
Enter "yes" here if your residence after leaving Germany was at least temporarily in an area with low taxation (low tax country).
If you answer "yes" to the question, your tax office will check whether there is an extended limited tax liability. In this case, after leaving Germany, you will still be subject to limited income tax for 10 years on all your income (taxation of capital appreciation on taking up residence abroad pursuant to sect. 2 of the Foreign Taxation Act (Außensteuergesetz)) which is not foreign income within the meaning of sect. 34c para. 1 of the Income Tax Act (EStG).
When does low taxation apply abroad?
A low-taxing area according to sect. 2, para. 2 of the Foreign Taxation Act (AStG) is a country in which the income tax for a single taxpayer with a notional taxable income of 77.000 Euro is more than one-third lower than in Germany. In addition, a low-taxing area may exist if the taxpayer is granted preferential taxation by the state.
In case of doubt, the Federal Central Tax Office will clarify whether the country in question is a low-tax country (see also the letter of the Federal Ministry of Finance dated 14.05.2004: Guidelines for the application of the Foreign Tax Act).
Enter data here only if you have moved away from Germany to another country in the course of 2022.
Tax deduction amounts according to sect. 50a of the Income Tax Act (EStG)
The following income of foreign payment creditors subject to limited tax liability (sect. 49 Income Tax Act (EStG)) is subject to the tax deduction procedure pursuant to sect. 50a of the Income Tax Act (EStG):
- Income generated by artistic, sporting, artistic, entertainment or similar performances (e.g. entrance fees, royalties, prize money, remuneration for participation in talk shows) and their domestic utilisation.
- Income from the transfer of rights utilised in Germany, for example, licences and copyrights (film rights, music rights, patent rights, etc.) but also of industrial, technical, scientific and similar experience, knowledge and skills ("know-how").
- Income from supervisory board duties in domestic companies.
The debtors of the remuneration paid are obligated to withhold, pay and declare taxes. The Federal Central Tax Office is responsible for carrying out the tax deduction procedure.
Did Partner A move to Germany or abroad in 2022?
Select "yes" if you moved to Germany or moved abroad in 2022. If this is not the case, select "no".
If you had your residence partially in Germany and partially abroad during the tax year, you were not fully taxable in Germany for the entire year. For the period that you lived in Germany, you are a fully taxable person.
The foreign income received beyond this period and which is not liable to German income tax is taken into account in the calculation of income tax (so-called "progression clause" (Progressionsvorbehalt)).
Did Partner A live abroad all year round in 2022?
Select "yes" if you had your residence or habitually resided abroad for the whole year 2022.
If you do not have a residence or do not habitually reside in Germany, you will be treated, upon application, as fully taxable if
- at least 90% of your income is subject to German income tax or
- if the income not subject to German income tax in 2022 does not exceed 10.347 Euro.
This amount will be reduced as follows depending on the group of countries:
- for countries in country group 2 by 25% to 7.761 Euro
- for countries in country group 3 by 50% to 5.174 Euro
- for countries in country group 4 by 75% to 2.587 Euro.
If you had your residence or habitually resided abroad during the tax year, received domestic income and wish to take advantage of the personal and family tax benefits, you must complete the following information in order to be treated as a fully taxable person in Germany.
This is also possible if your spouse was a resident or had a habitual residence in an EU/EEA country during the tax year, but you are a fully taxable person in Germany or treated as a fully taxable person upon application.
Did Partner B earn foreign income abroad in 2022?
Please select "yes" if the spouse earned income from abroad in 2022.
Income that is not subject to German income tax must be proven by a statement from the relevant tax authority in your home country. If you are a citizen of a member state of the European Union (EU) or of the EEA states Liechtenstein, Norway or Iceland and reside in one of these countries, use the form "Statement EU / EEA", otherwise the form "Statement outside EU / EEA".
Tax deductions on income (excluding pension income)
If you are subject to limited tax liability in Germany, tax deduction amounts will be withheld.
If you apply for unlimited tax liability, the tax deduction amounts already withheld are treated as advance payments.
You can only apply for unlimited tax liability if you also earn income in Germany. If you live abroad and continue to earn income in Germany, you are subject to limited tax liability.
In order to claim personal and family tax benefits, you must apply for unlimited tax liability.