Wie kann ich den Kinderfreibetrag in den ELStAM eintragen lassen?
Der Kinderfreibetrag wird zwar erst nachträglich gewährt, Sie können ihn jedoch in Ihren elektronischen Lohnsteuerabzugsmerkmalen (ELStAM) eintragen lassen. Zwar zahlen Sie dann nicht weniger Einkommensteuer voraus. Die unterjährige Belastung kann dennoch sinken. Denn der Kinderfreibetrag wird zur Berechnung von Kirchensteuer und Solidaritätszuschlag berücksichtigt, die dadurch geringer ausfallen. Sie müssen den Freibetrag bei Ihrem Finanzamt eintragen lassen. Dafür sollten Sie die folgenden Unterlagen mitbringen:
- Personalausweis oder Reisepass
- Lohnsteuerbescheinigung
- Abstammungsurkunde
- ggf. Vaterschaftsanerkennungsurkunde, wenn Sie nicht verheiratet sind
- ggf. Lebensbescheinigung für Kinder, die an einem anderen Wohnort gemeldet sind
Die Lebensbescheinigung darf nicht älter als drei Jahre sein. Wer die Lebensbescheinigung nicht vorlegen kann, z.B. weil das Kind im Ausland lebt, muss sich an sein Finanzamt wenden. Dort trägt der Finanzbeamte den Kinderfreibetrag ein.
Auch Eltern volljähriger Kinder müssen sich für die Eintragung von Freibeträgen an das Finanzamt wenden.
(2023): Wie kann ich den Kinderfreibetrag in den ELStAM eintragen lassen?
Steuerfreibeträge für Kinder zahlen sich aus
Da Kindern, ebenso wie den Eltern, jährliche Freibeträge bei der Einkommensbesteuerung zustehen, kann die Steuerlast völlig legal vermindert werden. Auch wenn bei den anhaltend niedrigen Zinsen der Sparerfreibetrag nicht mehr so schnell ausgeschöpft wird wie früher, sollten Eltern überlegen, inwieweit es sinnvoll ist, Kapitalerträge auf mehrere Schultern zu verteilen.
Bei einem Zins von 2,5 Prozent beispielsweise muss man über 40.000 Euro angelegen, um den Sparerpauschbetrag von 1.000 Euro zu überschreiten. Mit folgenden erhöhten Steuerbefreiungen können 2023 auch Kinder rechnen, wenn sie ausschließlich Einnahmen aus Kapitalvermögen haben:
- Grundfreibetrag 10.908 Euro
- Sparer-Pauschbetrag 1.000 Euro
- Sonderausgaben-Pauschbetrag 36 Euro
- Insgesamt steuerfrei (pro Kind) 11.944 Euro.
Das heißt: Zinsen, Dividenden und andere Einnahmen aus Kapitalvermögen, zu denen auch Gewinne aus der Veräußerung von nach 2008 erworbenen Wertpapieren gehören, sind bis zur Höhe von 11.184 Euro in diesem Jahr steuerfrei.
Die Schenkung von Kapitalvermögen an Kinder ist bis zu einem Betrag von 400.000 Euro pro Kind schenkungsteuerfrei. Eine Vermögensübertragung innerhalb der Familie erkennt die Finanzverwaltung jedoch nur an, wenn sie nicht allein aus Steuervermeidungsgründen vorgenommen wird. Die Schenkung muss also den zivilrechtlichen Vorschriften entsprechen und glaubhaft sein. Mindestvoraussetzung dafür ist ein Konto oder Depot auf den Namen des Kindes.
Zudem dürfen die Eltern nicht mehr ohne weiteres auf das verschenkte Kapital und dessen Zinsen für eigene Zwecke zurückgreifen. Zu berücksichtigen ist ferner, dass Kinder mit hohen Einkünften eigene Beiträge in die gesetzliche Krankenversicherung zahlen müssen. Auch für andere Fördermaßnahmen wie zum Beispiel BAföG sind bestimmte Einkommens- und Vermögensgrenzen zu beachten. Bei größeren, komplexeren Vermögensübertragungen ist es daher empfehlenswert, sich vorher unter rechtlichen und steuerlichen Aspekten beraten zu lassen.
(2023): Steuerfreibeträge für Kinder zahlen sich aus
Bekomme ich für alle Kinder gleich viel Kindergeld?
Wer mehrere Kinder hat, bekam früher nicht für jedes Kind gleich viel Kindergeld. Doch seit 2023 ist der Satz vereinheitlich worden. Der Anspruch auf Kindergeld beträgt:
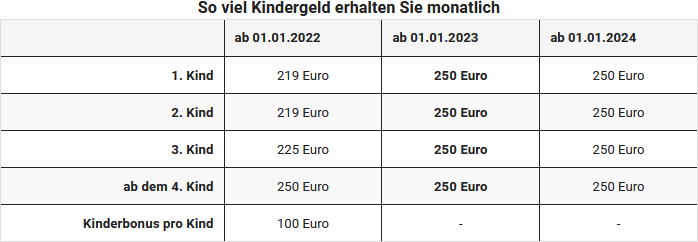
Für Kinder bis zur Vollendung des 18. Lebensjahres wird in jedem Fall Kindergeld gezahlt. Dabei spielt es keine Rolle, wie hoch das Einkommen des Kindes ist.
Für volljährige Kinder besteht der Anspruch weiter bis zum 25. Geburtstag, solange sie in Ausbildung sind oder einen Freiwilligendienst leisten. Das Kindergeld wird ausgezahlt durch die Familienkassen der Bundesagentur für Arbeit. Angehörige des öffentlichen Dienstes oder Empfänger von Versorgungsbezügen bekommen das Geld von ihren Arbeitgebern ausgezahlt.
Tipp
(2023): Bekomme ich für alle Kinder gleich viel Kindergeld?
Familien haben 2022 pro Kind einer 100-Euro-Kinderbonus erhalten
Mit dem "Steuerentlastungsgesetz 2022" wurde im Juli 2022 für jedes Kind ergänzend zum Kindergeld einmalig ein Kinderbonus von 100 Euro gezahlt.
- Ein Anspruch auf den Kinderbonus 2022 besteht für jedes Kind, für das im Juli 2022 ein Anspruch auf Kindergeld besteht. Kinder, für die im Juli 2022 kein Anspruch auf Kindergeld besteht, werden ebenfalls berücksichtigt, wenn für sie in einem anderen Monat des Jahres 2022 ein Kindergeldanspruch besteht.
- Der Kinderbonus wird auf den Kinderfreibetrag angerechnet. Das führt dazu, dass Familien mit hohem Einkommen, für die der Steuervorteil aus dem Kinderfreibetrag höher ist als das Kindergeld, davon nicht profitieren. Der Bonus wird im Rahmen der bei der Einkommensteuerveranlagung durchzuführenden Vergleichsberechnung gemäß § 31 Satz 4 EStG zusammen mit dem Kindergeld berücksichtigt. Bei dieser sogenannten Günstigerprüfung wird geprüft, ob sich Kindergeld und Kinderbonus oder die Entlastung aus dem Kinder- und Betreuungs-Freibetrag günstiger auswirken. Je höher das Einkommen ist, desto günstiger wirken die Freibeträge für Kinder. In diesen Fällen wird der Kinderbonus durch die allmählich einsetzende Besteuerung faktisch abgeschmolzen.
- Der Kinderbonus wird unabhängig von existenzsichernden Sozialleistungen gewährt. Der Einmalbetrag wird bei Sozialleistungen, deren Zahlung von anderen Einkommen abhängig ist, nicht als Einkommen berücksichtigt ("Gesetz zur Nichtanrechnung und Nichtberücksichtigung des Kinderbonus" vom 2.3.2009, das weiterhin gilt).
- Für den Einmalbetrag gelten ansonsten grundsätzlich alle Vorschriften, die auch für das - monatlich gezahlte -Kindergeld maßgebend sind. So kann zum Beispiel für jedes Kind nur einem Berechtigten der Einmalbetrag gezahlt werden. Für die Festsetzung des Einmalbetrags kann von der Erteilung eines schriftlichen Änderungsbescheides abgesehen werden.
(2023): Familien haben 2022 pro Kind einer 100-Euro-Kinderbonus erhalten
Habe ich nur bei meinen leiblichen Kindern einen Anspruch auf Kindergeld?
Nein. Kindergeldanspruch besteht für leibliche Kinder des Antragstellers und auch für dessen adoptierte Kinder. Für Pflegekinder können Sie Kindergeld beantragen, wenn diese in Ihrer Familie leben und ein dauerhaftes Aufsichts-, Betreuungs- und Erziehungsverhältnis besteht. Weiterhin darf das Obhuts- und Pflegeverhältnis zu den leiblichen Eltern nicht mehr bestehen. Gelegentliche Besuche der leiblichen Eltern sind unschädlich. Haben Sie Geschwister in Ihren Haushalt aufgenommen, besteht Anspruch auf Kindergeld, wenn sie Pflegekindern gleichgesetzt werden können.
Kindergeld wird auch gezahlt, wenn in Ihrem Haushalt ein Stief- oder Enkelkind lebt. In diesen Fällen liegt allerdings kein Kindschaftsverhältnis im Sinne des Steuerrechts vor. Deswegen steht Stief- oder Großeltern ein Kinderfreibetrag auch nicht automatisch zu, sondern erst, wenn die leiblichen Eltern die Freibeträge für Kinder in der Anlage K auf die neuen Bezugspersonen übertragen. Ist für Vollwaisen oder Kinder, die keine Kenntnis darüber haben, wo sich ihre Eltern aufhalten, keine andere Person bezugsberechtigt, können die Kinder selbst das Kindergeld erhalten. Sie bekommen dann den Betrag, der ihnen selbst für ein eigenes erstes Kind zustehen würde.
Haben Sie als Eltern ein Kind zur Adoption freigegeben, endet das Kindschaftsverhältnis zwischen Ihnen und dem Kind zu diesem Zeitpunkt. Gleichzeitig endet auch Ihr Anspruch auf Kindergeld und die steuerlichen Freibeträge.
Tipp
Für ein Kind, das Sie mit der Absicht, es zu adoptieren, in Ihren Haushalt aufgenommen haben, können Sie bereits vor der Adoption Kindergeld erhalten, denn es liegt in der Regel ein Pflegschaftsverhältnis vor.
(2023): Habe ich nur bei meinen leiblichen Kindern einen Anspruch auf Kindergeld?
Wie senke ich durch den Anspruch auf Kindergeld meine Kirchensteuer?
Die Höhe der Kirchensteuer richtet sich nach Ihrem Wohnort. Leben Sie in Bayern oder Baden-Württemberg, zahlen Kirchenangehörige 8 Prozent, in den übrigen Ländern 9 Prozent. Grundlage ist die festgesetzte Einkommensteuer. Sie zahlen folglich als Kirchensteuer 8 bzw. 9 Prozent Ihrer Einkommensteuer.
Beachten Sie: Die Kirchensteuer wird mit gleicher prozentualer Höhe auch im Rahmen der Abgeltungsteuer berücksichtigt. Sind bei Arbeitnehmern Kinderfreibeträge in ihren elektronischen Lohnsteuerabzugsmerkmalen (ELStAM) eingetragen, errechnet sich die monatliche Kirchensteuer aufgrund einer sogenannten fiktiven Lohnsteuer.
Kirchensteuer ohne Kinderfreibetrag:
Sie leben in Berlin und haben einen Brutto-Monatslohn von 3.000 Euro in der Steuerklasse IV. Ihre monatliche Kirchensteuer beträgt 31,44 Euro. Kirchensteuer mit zwei Kinderfreibeträgen: Sie leben in Berlin und haben einen Brutto-Monatslohn von 3.000 Euro bei Steuerklasse IV. Ihre monatliche Kirchensteuer beträgt nun 13,34 Euro.
Ist also in den ELStAM eine "Zahl der Kinderfreibeträge" eingetragen, verringert sich nicht die monatliche Lohnsteuer, sondern nur die monatliche Kirchensteuer sowie der monatliche Solidaritätszuschlag. Das gilt auch dann, wenn Sie während des Jahres Kindergeld erhalten.
In der Einkommensteuerveranlagung senken die Kinderfreibeträge das zu versteuernde Einkommen nur dann, wenn das Kindergeld nicht günstiger ist als der Steuervorteil. Doch zur Berechnung von Kirchensteuer (und Soli) werden die Kinderfreibeträge "fiktiv" abgezogen.
Vorteil: Auch wenn Kinder nur für einen Teil des Jahres zu berücksichtigen sind, werden für die Berechnung der Kirchensteuer und des Solidaritätszuschlages stets der volle Kinderfreibetrag und BEA-Freibetrag abgezogen. Dies kommt in Betracht bei Beendigung der Berufsausbildung oder Geburt eines Kindes.
(2023): Wie senke ich durch den Anspruch auf Kindergeld meine Kirchensteuer?
Wie hängen Kindergeld und Kinderfreibetrag zusammen?
Für die Freibeträge gelten die gleichen Voraussetzungen wie für den Anspruch auf Kindergeld: Es muss ein Kindschaftsverhältnis vorliegen, das Kind muss zu Ihrem Haushalt gehören und unter 18 sein bzw. die Bedingungen für den verlängerten Anspruch auf Kindergeld erfüllen.
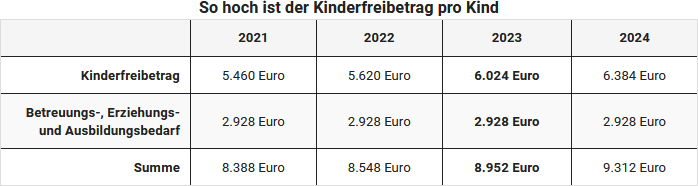
Der jährliche Kinderfreibetrag liegt im Jahre 2023 für Eltern, die steuerlich zusammen veranlagt werden, bei 6.024 Euro, der BEA-Freibetrag (für Betreuung, Erziehung und Ausbildung) bei 2.928 Euro. So steht Eltern für das Steuerjahr 2023 ein Freibetrag von insgesamt 8.952 Euro je Kind zu. Für getrennt Veranlagte bzw. Alleinstehende gilt, dass jeder Elternteil jeweils Anspruch auf den halben Freibetrag hat.
Günstigerprüfung
Diese Freibeträge werden im Rahmen der Steuerveranlagung aber nur gewährt, wenn die Steuerersparnis aus den Freibeträgen höher ist als das Kindergeld, wobei hier der Anspruch auf Kindergeld und nicht das tatsächlich erhaltene Kindergeld maßgebend ist. Ausrechnen muss man das allerdings nicht selbst. Das macht das Finanzamt, in der Steuersprache wird dieser Vorgang Günstigerprüfung genannt.
Achtung: In der Praxis gibt es zahlreiche Fälle, in denen die kindbedingten Vergünstigungen nicht gewährt werden, weil zwar ein anzurechnender "Anspruch auf Kindergeld" besteht, dieses de facto aber nicht gezahlt wurde. Und vor allem: Da die rückwirkende Auszahlung des Kindergeldes zudem per Gesetz auf sechs Monate begrenzt worden ist, kann oftmals auch das Kindergeld nicht mehr nachträglich realisiert werden. Anders ausgedrückt: Eltern, die vergessen haben, Kindergeld rechtzeitig zu beantragen, obwohl ihnen dieses zugestanden hätte, gehen nach derzeitiger Rechtslage (auch) bei der Einkommensteuer mehr oder weniger leer aus, da der "Anspruch auf Kindergeld“ angerechnet wird.
Dadurch wird das Existenzminimum der Kinder besteuert. Aktuell gibt es aber Licht am Ende des Tunnels: Sehr versteckt im "Gesetz gegen illegale Beschäftigung und Sozialleistungsmissbrauch“ befindet sich eine gesetzliche Änderung, die die kindbedingten Vergünstigungen bei der Einkommensteuer betrifft. Aufgrund einer Änderung des § 31 EStG kommt es nun nicht mehr auf das zustehende, sondern auf das ausgezahlte Kindergeld an, wenn das Kindergeld zu spät beantragt worden und es damit nicht zur Auszahlung gekommen ist. Betroffene können dann wenigstes von den Freibeträgen bei der Steuerveranlagung profitieren.
(2023): Wie hängen Kindergeld und Kinderfreibetrag zusammen?
Wie lange habe ich rückwirkend Anspruch auf Kindergeld?
Um Kindergeld zu erhalten, ist ein Antrag zwingend erforderlich. Das Kindergeld ist stets schriftlich bei der zuständigen Familienkasse zu beantragen.
Vorsicht: Seit dem 1.1.2018 gilt für das Kindergeld eine spezielle Verjährungsregel mit einer Auszahlungsbeschränkung. Damit wurde die Auszahlungsfrist erheblich verkürzt: Das Kindergeld wird seither statt für die letzten vier Jahre rückwirkend nur für die letzten sechs Monate vor Beginn des Monats gezahlt, in dem der Antrag auf Kindergeld eingegangen ist.
Für die Berechnung der Freibeträge ist es unerheblich, ob Sie tatsächlich Kindergeld erhalten haben oder nicht. Wenn das Finanzamt im Rahmen der Günstigerprüfung die Höhe von Kindergeld und Kinderfreibetrag vergleicht, wird nicht Ihr tatsächlich erhaltenes Kindergeld erfasst, sondern lediglich Ihr Anspruch (siehe aber zur Neuregelung den Hinweis unten).
Bei der Einkommensteuerveranlagung prüft das Finanzamt, ob die Steuerersparnis aus dem Kinderfreibetrag und dem BEA-Freibetrag höher ist als das Kindergeld. Ist das der Fall, werden die Freibeträge berücksichtigt. Das Kindergeld wird dann bei der Berechnung der festzusetzenden Einkommensteuer hinzugerechnet.
Sind die Freibeträge geringer als das Kindergeld, bleibt es beim Kindergeld. Das Kindergeld ist also eine Art Vorauszahlung auf den möglichen Steuervorteil. Im Rahmen der Günstigerprüfung wird der Anspruch auf Kindergeld zugrunde gelegt, auch wenn faktisch kein Kindergeld ausgezahlt wurde. Auf diese Weise muss der Steuerbescheid nicht geändert werden, falls die Eltern einen Antrag auf Kindergeld nachträglich stellen.
Derzeit müssen Sie als Eltern also immer zuerst den Antrag auf Kindergeld stellen, auch wenn Sie darauf spekulieren, dass für Sie die Freibeträge günstiger ausfallen. Das Kindergeld wird in jedem Fall der Einkommensteuer hinzugerechnet.
Achtung: In der Praxis gibt es zahlreiche Fälle, in denen die kindbedingten Vergünstigungen nicht gewährt werden, weil zwar ein anzurechnender "Anspruch auf Kindergeld" besteht, dieses de facto aber nicht gezahlt wurde. Und vor allem: Da die rückwirkende Auszahlung des Kindergeldes zudem per Gesetz auf sechs Monate begrenzt worden ist, kann oftmals auch das Kindergeld nicht mehr nachträglich realisiert werden. Anders ausgedrückt: Eltern, die vergessen haben, Kindergeld rechtzeitig zu beantragen, obwohl ihnen dieses zugestanden hätte, gehen nach derzeitiger Rechtslage (auch) bei der Einkommensteuer mehr oder weniger leer aus, da der "Anspruch auf Kindergeld“ angerechnet wird. Dadurch wird das Existenzminimum der Kinder besteuert. Aktuell gibt es aber Licht am Ende des Tunnels: Sehr versteckt im "Gesetz gegen illegale Beschäftigung und Sozialleistungsmissbrauch“ befindet sich eine gesetzliche Änderung, die die kindbedingten Vergünstigungen bei der Einkommensteuer betrifft. Aufgrund einer Änderung des § 31 EStG kommt es nun nicht mehr auf das zustehende, sondern auf das ausgezahlte Kindergeld an, wenn das Kindergeld zu spät beantragt worden und es damit nicht zur Auszahlung gekommen ist. Betroffene können dann wenigstes von den Freibeträgen bei der Steuerveranlagung profitieren.
Steuertipp für Altfälle: § 66 Abs. 3 EStG hieß es bis Mitte 2019: "Das Kindergeld wird rückwirkend nur für die letzten sechs Monate vor Beginn des Monats gezahlt, in dem der Antrag auf Kindergeld eingegangen ist." Nun gab es reichlich Fälle, in denen Kindergeld zum Beispiel im Januar 2018 rückwirkend für das ganze Jahr 2017 festgesetzt, aber eben nur für sechs Monate ausgezahlt wurde. Die Finanzverwaltung und die Familienkassen haben die Vorschrift jedenfalls in diesem Sinne ausgelegt.
Doch so geht es nicht! Der Bundesfinanzhof hat dem Fiskus und vor allem den Familienkassen die Leviten gelesen: Wenn Kindergeld festgesetzt wird, ist es auch auszuzahlen. Die Familienkassen hätten das Kindergeld halt nur für sechs Monate festsetzen dürfen. (BFH-Urteil vom 19.2.2020, III R 66/18).
- Der Fall: Der Kläger ist der Vater einer im Februar 1997 geborenen Tochter. In einem bereits 2015 gestellten Antrag gab der Kläger an, dass seine Tochter ab September 2015 eine Ausbildung zur Erzieherin aufnehmen wolle. Die Familienkasse setzte daraufhin zunächst Kindergeld fest, hob die Kindergeldfestsetzung aber im Juli 2015 mangels Vorlage eines Ausbildungsnachweises wieder auf. Mit einem dann erst im April 2018 bei der Familienkasse eingegangenen Antrag begehrte der Kläger erneut Kindergeld, dieses Mal sogar bereits für den Zeitraum ab August 2015. Die Familienkasse setzte in einem Bescheid vom April 2018 laufendes Kindergeld ab dem Monat August 2015 fest. Die Nachzahlung von Kindergeld beschränkte sie jedoch auf den Zeitraum von Oktober 2017 bis April 2018 (= sechs Monate). Das Finanzgericht gab der dagegen gerichteten Klage statt und erkannte einen Nachzahlungsanspruch auch für die Monate August 2015 bis September 2017 an.
- Der BFH stimmt der Vorinstanz zu. Da die Familienkasse im Streitfall das Kindergeld über den Sechs-Monats-Zeitraum hinaus rückwirkend festgesetzt hatte, hielt sie der BFH auch für verpflichtet, das Kindergeld in diesem Umfang an den Kläger auszuzahlen.
(2023): Wie lange habe ich rückwirkend Anspruch auf Kindergeld?
Welche dem Kindergeld vergleichbaren Leistungen muss ich angeben?
Generell steht allen Eltern Kindergeld zu, es gibt jedoch Ausnahmen, wenn Sie als Eltern schon andere finanzielle Leistungen erhalten. Diese müssen Sie hier in dieses Formular eintragen.
Besteht für Sie ein Anspruch auf Kinderzulage aus der gesetzlichen Unfallversicherung oder einer gesetzlichen Rentenversicherung, steht Ihnen kein Kindergeld mehr zu. Werden dem Kind im Ausland oder von einer zwischen- oder überstaatlichen Einrichtung Leistungen gezahlt, die mit dem Kindergeld vergleichbar sind, können Sie ebenfalls kein Kindergeld beanspruchen. Das Kind kann allerdings als Zählkind dazu beitragen, dass sich der Kindergeldanspruch für weitere Kinder erhöht.
Wenn der Kinderzuschuss oder die Kinderzulage zur Rente niedriger sind als das Kindergeld, wird die Differenz als Teilkindergeld gezahlt. Dies betrifft auch Leistungen, die Sie von einem anderen Mitgliedstaat der Europäischen Union, des Europäischen Wirtschaftsraumes oder der Schweiz erhalten.
Wichtig: Ansprüche auf Kindergeld müssen Sie auch angeben, wenn Sie im betreffenden Jahr gar kein Kindergeld erhalten haben. Beispielsweise, wenn Ihr Kind im Dezember eines Jahres geboren wurde, Sie das erste Kindergeld jedoch erst im Folgejahr erhalten. Auch wenn Sie getrennt leben und kein Kindergeld erhalten, weil dies zur Berechnung Ihrer Unterhaltsverpflichtung hinzugezogen wurde, müssen Sie die Hälfte des Kindergeldes als Ihren Anspruch angeben.
(2023): Welche dem Kindergeld vergleichbaren Leistungen muss ich angeben?
Mein Kind lebt bei meinem Ex-Partner, muss ich trotzdem Kindergeld angeben?
Wenn für ein Kind Anspruch auf Kindergeld besteht, bekommt der betreuende Elternteil das Kindergeld ausbezahlt. Wenn Sie jedoch von Ihrem Partner getrennt leben und dem Kind gegenüber unterhaltspflichtig sind, wird zur Berechnung des Unterhalts das Kindergeld zur Hälfte hinzugerechnet. Auf diese Weise profitieren Sie indirekt von der Hälfte des Kindergeldes.
Sie müssen deshalb in Ihrer Steuererklärung die Hälfte des Ihnen zustehenden Kindergeldes angeben. Von den 250 Euro monatlichem Kindergeld, das Ihnen im Jahr 2023 zustehen würde, tragen Sie also monatlich 125 Euro ein. Sind Sie das ganze Jahr über getrennt gewesen und hat der betreuende Elternteil in der gesamten Zeit das Kindergeld erhalten, geben Sie für 2023 für das erste Kind 1.500 Euro (12 mal 125 Euro) an.
Hierzu ist es unwesentlich, ob Sie den vollen Unterhalt laut „Düsseldorfer Tabelle“ zahlen oder einen reduzierten Satz.
Tipp
Selbst wenn Sie als unterhaltspflichtiger Elternteil offiziell auf die Anrechnung des halben Kindergeldes verzichtet haben, wird Ihr Anspruch auf das halbe Kindergeld in die Günstigerprüfung mit einbezogen, in der das Finanzamt berechnet, ob das Kindergeld oder die Freibeträge vorteilhafter für Sie sind.
(2023): Mein Kind lebt bei meinem Ex-Partner, muss ich trotzdem Kindergeld angeben?
Was ist der Kinderfreibetrag?
Kindergeld und Kinderfreibetrag sind eine Steuerentlastung für die Ausgaben, die den Eltern durch die Kinder entstehen. Der Anspruch auf Kindergeld besteht von Geburt an automatisch, muss aber schriftlich beantragt werden. Es sind nicht - wie oftmals angenommen - die Kinder, die Anspruch auf das Kindergeld haben, sondern die Eltern bzw. Erziehungsberechtigten, die für das Wohl des Kindes verantwortlich sind.
Kindergeld
Das Kindergeld ist ein monatlich ausgezahlter Betrag, den Eltern meist von der Familienkasse überwiesen bekommen. Das Kindergeld muss nicht versteuert werden. Die Höhe des Kindergeldes richtet sich nach der Anzahl der Kinder.

Kinderfreibetrag
Der Kinderfreibetrag wird im Gegensatz zum Kindergeld nicht ausgezahlt. Der Freibetrag wird vom zu versteuernden Einkommen abgezogen. Dadurch wirkt er sich steuermindernd bei der Berechnung der Einkommensteuer aus. Das monatlich bereits ausgezahlte Kindergeld stellt eine Vorauszahlung auf den Kinderfreibetrag dar. Im Jahr 2023 beträgt der Kinderfreibetrag 6.024 Euro für zusammen veranlagte Eltern, ansonsten 3.012 Euro je Elternteil. Der BEA-Freibetrag (für Betreuungs-, Erziehungs- und Ausbildungsbedarf) beträgt 2.928 Euro.
Kindergeld und Kinderfreibetrag sind miteinander gekoppelt. Ob das Kindergeld oder der Kinderfreibetrag am Ende eines Steuerjahres für den Steuerpflichtigen günstiger ist, ermittelt das Finanzamt automatisch durch eine Günstigerprüfung.
Anspruch auf Kinderfreibetrag bzw. Kindergeld
Anspruch auf den Kinderfreibetrag haben die Erziehungsberechtigten von der Geburt des Kindes bis zum
- 18. Lebensjahr.
- 25. Lebensjahr, wenn sich das Kind noch in Ausbildung oder Studium befindet oder einen Freiwilligendienst leistet.
Wenn das Kind behindert ist und außerstande, sich selbst zu unterhalten, besteht der Anspruch auf Kindergeld oder Kinderfreibetrag zeitlich unbegrenzt.

(2023): Was ist der Kinderfreibetrag?
Wie viel Kindergeld kann ich bekommen?
Das Kindergeld war früher nach der Anzahl der Kinder gestaffelt, beträgt nun aber einheitlich 250 Euro je Kind.:

Für minderjährige Kinder bis zur Vollendung des 18. Lebensjahres wird in jedem Fall Kindergeld gezahlt. Für volljährige Kinder besteht der Anspruch weiter bis zum 25. Geburtstag, solange sie in Ausbildung sind oder einen Freiwilligendienst leisten. Das Kindergeld wird ausgezahlt durch die Familienkassen der Bundesagentur für Arbeit. Angehörige des öffentlichen Dienstes oder Empfänger von Versorgungsbezügen bekommen das Geld i. d. R. direkt von ihren Arbeitgebern ausgezahlt.
(2023): Wie viel Kindergeld kann ich bekommen?
Existenzminimum: Sind die Kinderfreibeträge verfassungswidrig zu niedrig?
Das Existenzminimum von Kindern muss aus verfassungsrechtlichen Gründen von der Steuer freigestellt werden. Dies geschieht durch den Kinderfreibetrag und den BEA-Freibetrag (für Betreuung, Erziehung und Ausbildungsbedarf). Das Finanzamt prüft automatisch, ob diese Freibeträge oder das während des Jahres ausbezahlte Kindergeld günstiger sind.
Der BEA-Freibetrag beträgt 2.928 Euro; der Kinderfreibetrag 6.024 Euro (Jahr 2023).
Das Finanzgericht Niedersachsen äußerte ernsthafte Zweifel an der Verfassungsmäßigkeit des Kinderfreibetrags für das Jahr 2014, was zu einer Aufhebung der Vollziehung führte. Auch der Bundesfinanzhof stimmte dem teilweise zu (Niedersächsisches FG vom 16.2.2016, 7 V 237/15).
Aktuell hat das Finanzgericht Niedersachsen die Berechnungsmethode des Kinderfreibetrags als verfassungswidrig eingestuft und dem Bundesverfassungsgericht die Frage vorgelegt. Die Richter bemängeln, dass der Kinderfreibetrag altersunabhängig ist, obwohl die sozialhilferechtlichen Regelbedarfe für Kinder altersabhängig sind. Sie fordern eine Erhöhung des Kinderfreibetrags (FG Niedersachsen vom 2.12.2016, 7 K 83/16).
Die Entscheidung des Bundesverfassungsgerichts könnte bis zu zehn Jahre dauern und betrifft Eltern, die Kindergeld oder einen Kinderfreibetrag erhalten, da eine Erhöhung der Kinderfreibeträge sich auf die Kirchensteuer und den Solidaritätszuschlag auswirkt.
(2023): Existenzminimum: Sind die Kinderfreibeträge verfassungswidrig zu niedrig?






