How can I have the child allowance entered in the ELStAM?
The child allowance is granted retrospectively, but you can have it entered in your electronic wage tax deduction features (ELStAM). Although you will not pay less income tax in advance, the mid-year burden may still decrease. This is because the child allowance is taken into account when calculating church tax and the solidarity surcharge, which are then reduced. You must have the allowance entered at your tax office. You should bring the following documents:
- Identity card or passport
- Wage tax certificate
- Birth certificate
- If applicable, paternity recognition certificate if you are not married
- If applicable, certificate of life for children registered at a different address
The certificate of life must not be older than three years. If you cannot provide the certificate of life, e.g. because the child lives abroad, you must contact your tax office. The tax officer will enter the child allowance there.
Parents of children over 18 must also contact the tax office to have allowances entered.
(2024): How can I have the child allowance entered in the ELStAM?
Child tax allowances pay off
Children, like their parents, are entitled to annual allowances for income tax. These allowances can legally reduce the tax burden. Particularly with capital gains, a strategic distribution within the family can bring tax advantages. Despite still moderate interest rates, it is worth exploring this option.
Capital Gains and Tax Allowances 2024
To fully utilise the saver’s allowance of 1.000 Euro at an interest rate of 2.5%, approximately 40.000 Euro would need to be invested. Parents should check whether capital gains can be transferred to the children to benefit from their tax allowances. Children can use the following tax allowances in 2024, provided they only have income from capital assets:
- Basic allowance 11.784 Euro
- Saver’s allowance 1.000 Euro
- Special expenses allowance 36 Euro
- Total tax-free (per child) 12.820 Euro.
This means: Capital gains such as interest, dividends, or profits from the sale of securities are tax-free up to an amount of 12.820 Euro.
Gifts of Capital Assets to Children
Parents can transfer capital assets to their children tax-free up to an amount of 400.000 Euro per child. However, the transfer of assets must comply with civil law regulations and not be solely for tax avoidance. To ensure this, the following points must be observed:
- The capital must be deposited into the child's account or portfolio.
- Parents must no longer have unrestricted access to the capital or its returns.
- The gift must be credible and documented.
Additional Aspects for High Capital Income
Children with high capital gains may need to make their own contributions to statutory health insurance. Additionally, such income can affect benefits like BAföG, as certain income and asset limits must be observed. Therefore, it is advisable to have larger asset transfers reviewed for tax and legal implications.
(2024): Child tax allowances pay off
Do I receive the same amount of child benefit for all children?
In the past, if you had multiple children, you did not receive the same amount of child benefit for each child. However, since 2023, the rate has been standardised. The entitlement to child benefit is:
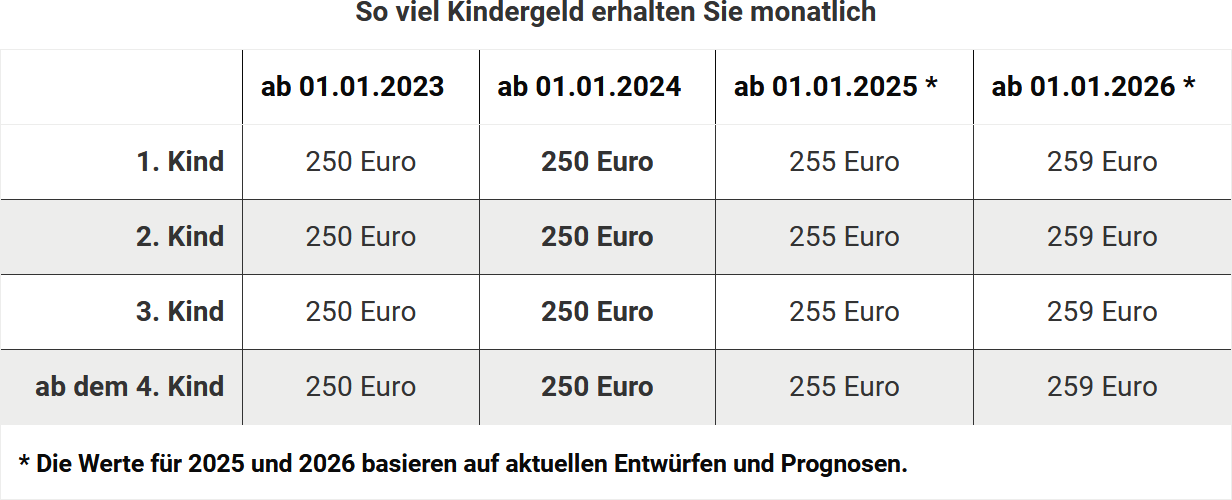
Child benefit is paid for children up to the age of 18. The child's income is irrelevant.
The entitlement continues for children over 18 until their 25th birthday, as long as they are in education or doing voluntary service. Child benefit is paid by the family benefits offices of the Federal Employment Agency. Public sector employees or recipients of pension payments receive the money from their employers.
Tipp
(2024): Do I receive the same amount of child benefit for all children?
Families received a 100-Euro child bonus per child in 2022
With the "Tax Relief Act 2022", a one-off child bonus of 100 Euro was paid in July 2022 in addition to child benefit for each child.
- There is an entitlement to the child bonus 2022 for each child for whom there is an entitlement to child benefit in July 2022. Children for whom there is no entitlement to child benefit in July 2022 are also considered if there is an entitlement to child benefit for them in another month of 2022.
- The child bonus is offset against the child allowance. This means that families with high incomes, for whom the tax advantage from the child allowance is higher than the child benefit, do not benefit from it. The bonus is taken into account together with the child benefit in the comparative calculation to be carried out as part of the income tax assessment in accordance with § 31 sentence 4 EStG. In this so-called favourable assessment, it is checked whether child benefit and child bonus or the relief from the child and care allowance have a more favourable effect. The higher the income, the more favourable the allowances for children are. In these cases, the child bonus is effectively reduced by the gradually increasing taxation.
- The child bonus is granted independently of subsistence-level social benefits. The one-off payment is not considered as income for social benefits whose payment depends on other income ("Act on the Non-Credit and Non-Consideration of the Child Bonus" of 2.3.2009, which still applies).
- Otherwise, all regulations that apply to the - monthly paid - child benefit also apply to the one-off payment. For example, the one-off payment can only be paid to one beneficiary per child. A written notice of amendment may be waived for the determination of the one-off payment.
(2024): Families received a 100-Euro child bonus per child in 2022
Do I only have a child benefit entitlement for my biological children?
No. Child benefit entitlement exists for the applicant's biological children and also for their adopted children. You can apply for child benefit for foster children if they live in your family and there is a permanent relationship of supervision, care, and upbringing. Furthermore, the custody and care relationship with the biological parents must no longer exist. Occasional visits from the biological parents are harmless. If you have taken siblings into your household, you are entitled to child benefit if they can be equated with foster children.
Child benefit is also paid if a stepchild or grandchild lives in your household. In these cases, however, there is no child relationship in the sense of tax law. Therefore, step- or grandparents are not automatically entitled to a child allowance, but only when the biological parents transfer the child allowances to the new guardians in Form K. If orphans or children who do not know where their parents are have no other person entitled to receive it, the children themselves can receive the child benefit. They then receive the amount that would be due to them for their own first child.
If you as parents have given a child up for adoption, the child relationship between you and the child ends at that time. Your entitlement to child benefit and tax allowances also ends at the same time.
Tip
For a child you have taken into your household with the intention of adopting, you can receive child benefit even before the adoption, as there is usually a foster relationship.
(2024): Do I only have a child benefit entitlement for my biological children?
How can I reduce my church tax by claiming child benefit?
The amount of church tax depends on your place of residence. In Bavaria and Baden-Württemberg, church members pay 8 percent of the assessed income tax, while in other federal states it is 9 percent.
Please note: Church tax is also taken into account at the same rate for capital gains tax. For employees with child allowances in the electronic wage tax deduction features (ELStAM), church tax is calculated based on a so-called notional wage tax.
Beispiel
Church tax without child allowance: You live in Berlin and have a gross monthly salary of 3.000 Euro in tax class IV. Your monthly church tax is 29.63 Euro.
Church tax with two child allowances: You live in Berlin and have a gross monthly salary of 3.000 Euro in tax class IV. Your monthly church tax is now 11.21 Euro.
Important: Child allowances do not reduce the monthly income tax, but only reduce the monthly church tax and solidarity surcharge. This also applies if you receive child benefit at the same time.
Child allowances in the income tax return
In the income tax assessment, child allowances only reduce the taxable income if the tax advantage is greater than the child benefit received. However, for the calculation of church tax and the solidarity surcharge, the allowances are taken into account "notionally".
Advantage in case of mid-year change
Even if children are only to be considered for part of the year (e.g. in the case of birth or end of education), the full child allowance is always deducted for church tax and the solidarity surcharge.
(2024): How can I reduce my church tax by claiming child benefit?
How are child benefit and the child allowance related?
For the allowances, the same conditions apply as for the entitlement to child benefit: there must be a parental relationship, the child must belong to your household and be under 18 or meet the conditions for the extended entitlement to child benefit.
The annual child allowance for parents who are jointly assessed for tax purposes is 6,612 Euro, and the BEA allowance (for care, education and training) is 2,928 Euro. Thus, parents are entitled to a total allowance of 9,540 Euro per child for the tax year 2024. For separately assessed or single parents, each parent is entitled to half of the allowance.

Favourability test
These allowances are only granted as part of the tax assessment if the tax saving from the allowances is higher than the child benefit, whereby the entitlement to child benefit and not the actual child benefit received is decisive. However, you do not have to calculate this yourself. The tax office does this, and in tax language, this process is called the favourability test.
Note: In practice, there are numerous cases where child-related benefits are not granted because there is an "entitlement to child benefit" to be credited, but this has not actually been paid. And above all: Since the retroactive payment of child benefit has also been legally limited to six months, it is often no longer possible to realise the child benefit retrospectively. In other words, parents who forgot to apply for child benefit in time, even though they were entitled to it, are more or less left empty-handed under the current legal situation, as the "entitlement to child benefit" is credited.
As a result, the children's subsistence level is taxed. However, there is currently light at the end of the tunnel: Very hidden in the "Act against Illegal Employment and Benefit Fraud" is a legal change affecting child-related benefits in income tax. Due to an amendment to § 31 EStG, it is now no longer the entitled but the paid child benefit that counts if the child benefit was applied for too late and therefore not paid. Those affected can then at least benefit from the allowances in the tax assessment.
(2024): How are child benefit and the child allowance related?
How far back can I claim child benefit?
To receive child benefit, an application is mandatory. Child benefit must always be applied for in writing at the relevant family benefits office.
Note: Since 1 January 2018, a special limitation rule with a payout restriction applies to child benefit. The payout period has been significantly shortened: child benefit is now paid retroactively for only the last six months before the beginning of the month in which the application for child benefit was received, instead of the last four years.
For the calculation of allowances, it is irrelevant whether you have actually received child benefit or not. When the tax office compares the amount of child benefit and child allowance as part of the favourable assessment, it does not record the child benefit you actually received, but only your entitlement (see the note on the new regulation below).
During the income tax assessment, the tax office checks whether the tax saving from the child allowance and the BEA allowance is higher than the child benefit. If this is the case, the allowances are taken into account. The child benefit is then added to the calculation of the income tax to be assessed.
If the allowances are lower than the child benefit, the child benefit remains. Child benefit is therefore a kind of advance payment on the possible tax advantage. As part of the favourable assessment, the entitlement to child benefit is taken as the basis, even if no child benefit was actually paid out. In this way, the tax assessment does not have to be changed if the parents submit an application for child benefit retrospectively.
Currently, as parents, you must always first apply for child benefit, even if you speculate that the allowances will be more favourable for you. In any case, the child benefit is added to the income tax.
Attention: In practice, there are numerous cases in which child-related benefits are not granted because there is an "entitlement to child benefit" to be credited, but this has not actually been paid. And above all: Since the retroactive payment of child benefit has also been legally limited to six months, child benefit can often no longer be realised retrospectively. In other words, parents who forgot to apply for child benefit in time, even though they were entitled to it, are more or less left empty-handed under the current legal situation, as the "entitlement to child benefit" is credited. This means that the children's subsistence level is taxed. However, there is currently light at the end of the tunnel: Very hidden in the "Act against Illegal Employment and Social Benefit Fraud" is a legal change that affects child-related benefits in income tax. Due to an amendment to Section 31 of the Income Tax Act, it is now no longer the child benefit to which you are entitled that counts, but the child benefit paid out if the child benefit was applied for too late and therefore not paid out. Those affected can then at least benefit from the allowances in the tax assessment.
Tax tip for old cases: Until mid-2019, Section 66 (3) of the Income Tax Act stated: "Child benefit is paid retroactively only for the last six months before the beginning of the month in which the application for child benefit was received." There were plenty of cases where child benefit was, for example, retroactively granted in January 2018 for the whole of 2017, but only paid out for six months. In any case, the tax authorities and the family benefits offices interpreted the regulation in this way.
But that's not how it works! The Federal Fiscal Court has reprimanded the tax authorities and especially the family benefits offices: If child benefit is granted, it must also be paid out. The family benefits offices should have only granted child benefit for six months. (BFH ruling of 19 February 2020, III R 66/18).
- The case: The claimant is the father of a daughter born in February 1997. In an application already submitted in 2015, the claimant stated that his daughter intended to start training as an educator in September 2015. The family benefits office initially granted child benefit, but revoked the child benefit approval in July 2015 due to the lack of proof of training. With an application received by the family benefits office in April 2018, the claimant again requested child benefit, this time even for the period from August 2015. In a notice dated April 2018, the family benefits office granted ongoing child benefit from August 2015. However, it limited the back payment of child benefit to the period from October 2017 to April 2018 (= six months). The tax court upheld the claim against this and recognised a back payment claim for the months August 2015 to September 2017.
- The BFH agreed with the lower court. As the family benefits office had retroactively granted child benefit beyond the six-month period in the case in dispute, the BFH also considered it obliged to pay the child benefit to the claimant to this extent.
(2024): How far back can I claim child benefit?
Which benefits comparable to child benefit must I declare?
In general, all parents are entitled to child benefit, but there are exceptions if other financial benefits are received. You must declare these on the relevant form.
Exceptions to child benefit entitlement
- If you receive child allowances from statutory accident insurance or pension insurance, you are not entitled to child benefit.
- If comparable benefits are paid abroad or by an intergovernmental or supranational institution, the entitlement to child benefit lapses.
Partial child benefit
If the child supplement or child allowance for the pension is lower than the child benefit, the difference is paid as partial child benefit. This also applies to comparable benefits from another EU country, the European Economic Area or Switzerland.
Standardised child benefit and abolition of "counting children"
As of 1 January 2023, the graduated child benefit rates have been abolished. Previously, the amount of child benefit depended on the number of children – from the third child onwards, the child benefit was higher. Now a standard amount of 250 Euro per month applies for each child.
This also eliminates the role of "counting children". Counting children are children who do not receive child benefit directly but were taken into account when calculating the amount. This regulation was particularly relevant for patchwork families or children from previous relationships.
Further notes:
- Claims to child benefit must also be declared if you did not receive child benefit in the relevant year, for example, if the child was born in December and the child benefit is paid in the following year.
- If child benefit is used in the maintenance calculation, separated parents must each declare half of the child benefit as a claim.
(2024): Which benefits comparable to child benefit must I declare?
Do I still need to declare child benefit if my child lives with my ex-partner?
If you are entitled to child benefit for a child, the parent who looks after the child receives the child benefit payments. However, if you are separated from your partner and have maintenance obligations towards the child, half of the child benefit is added to the maintenance calculation. This way, you indirectly benefit from half of the child benefit.
Therefore, you must declare half of the child benefit you are entitled to in your tax return. Of the 250 Euro monthly child benefit you would be entitled to in the year 2024, you enter 125 Euro per month. If you were separated for the entire year and the parent looking after the child received the child benefit for the entire period, you enter 1,500 Euro (12 times 125 Euro) for 2024 for the first child.
It is irrelevant whether you pay the full maintenance according to the „Düsseldorf Table“ or a reduced rate.
Tip
Even if you, as the parent obliged to pay maintenance, have officially waived the crediting of half the child benefit, your entitlement to half the child benefit is included in the favourable assessment, in which the tax office calculates whether the child benefit or the allowances are more advantageous for you.
(2024): Do I still need to declare child benefit if my child lives with my ex-partner?
What is the child allowance?
Child benefit and child allowance are tax reliefs for expenses incurred by parents due to their children. The entitlement to child benefit exists automatically from birth but must be applied for in writing. It is not the children who are entitled to child benefit, but the parents or guardians responsible for the child's welfare.
Child benefit
Child benefit is a monthly payment that parents usually receive from the family benefits office. Child benefit is not taxable. The amount of child benefit depends on the number of children.

Child allowance
In contrast to child benefit, the child allowance is not paid out. The allowance is deducted from taxable income, thereby reducing income tax. The child benefit already paid monthly is an advance payment on the child allowance. In 2023, the child allowance is 6.024 Euro for jointly assessed parents, otherwise 3.012 Euro per parent. The BEA allowance (for care, education, and training needs) is 2.928 Euro.
Child benefit and child allowance are linked. The tax office automatically determines whether child benefit or the child allowance is more favourable for the taxpayer at the end of a tax year through a favourable assessment.
Entitlement to child allowance or child benefit
Parents are entitled to the child allowance from the birth of the child until the
- 18th birthday.
- 25th birthday if the child is still in education or training or doing voluntary service.
If the child is disabled and unable to support themselves, the entitlement to child benefit or child allowance is unlimited.

(2024): What is the child allowance?
How much child benefit can I receive?
Child benefit was previously staggered according to the number of children, but is now a flat rate of 250 Euro per child.

Child benefit is paid for children under 18 in all cases. For children over 18, the entitlement continues until their 25th birthday, as long as they are in education or doing voluntary service. Child benefit is paid by the family offices of the Federal Employment Agency. Public sector employees or recipients of pension payments usually receive the money directly from their employers.
(2024): How much child benefit can I receive?
Minimum standard of living: Are the child allowances unconstitutionally low?
The minimum subsistence level for children must be exempt from tax for constitutional reasons. This is done through the child allowance and the BEA allowance (for care, education and training needs). The tax office automatically checks whether these allowances or the child benefit paid during the year are more favourable.
The Lower Saxony Fiscal Court expressed serious doubts about the constitutionality of the child allowance for 2014, which led to a suspension of execution. The Federal Fiscal Court partially agreed (Lower Saxony FG of 16.2.2016, 7 V 237/15).
However, the Federal Constitutional Court declared the judicial submission by the Lower Saxony FG to be inadmissible (BVerfG, decision of 5.9.2024 - 2 BvL 3/17; published on 2.10.2024).
(2024): Minimum standard of living: Are the child allowances unconstitutionally low?






