What is a private pension?
In the "Private pensions" section, all lifelong annuities from private pension insurance are recorded, as well as certain fixed-term pensions, e.g.
- survivor's pensions,
- occupational disability pensions, and
- incapacity pensions
(2024): What is a private pension?
How is a private pension taxed?
Private annuities are always taxed based on the yield percentage. The amount of the taxable yield percentage depends on the age of the beneficiary at the start of the annuity payments. The yield percentage determined in this way is, for example, at the start of the annuity after the age of...
... 60: 22%
... 61: 22%
... 62: 21%
... 63: 20%
... 64: 19%
... 65: 18%
If these annuities are limited to a specific term, the special yield percentage according to § 55 EStDV applies. The yield percentage in this case does not depend on the age at the start of the annuity, but on the duration of the payments. For a term of for example ten years, the special yield percentage is 12% of the annuity payments.
(2024): How is a private pension taxed?
What is the income share of the pension?
The percentage of income depends on the age of the pension beneficiary at the start of the pension (§ 22 No. 1 Sentence 3 EStG). The following table shows the percentage of income based on the age at the start of the pension:
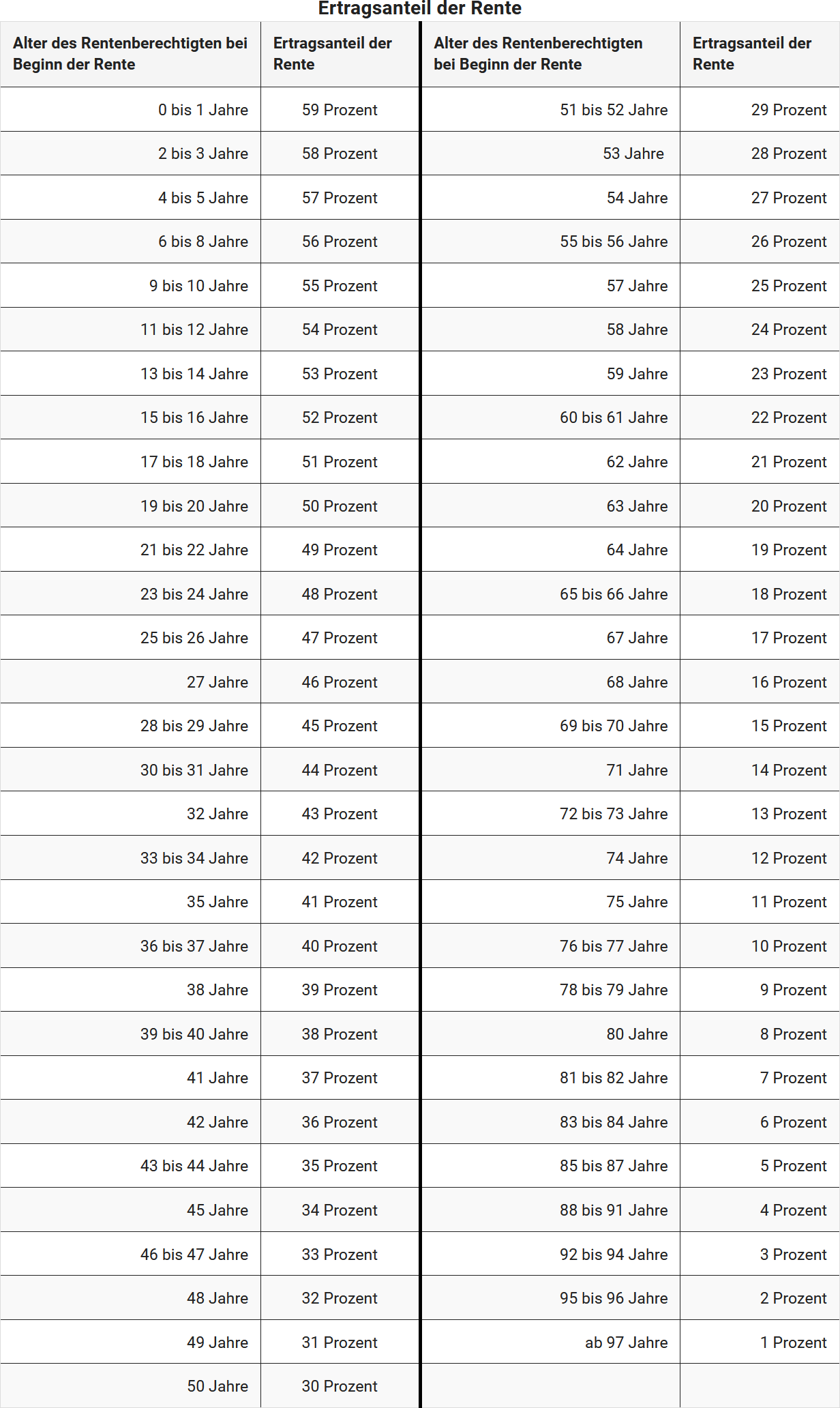
(2024): What is the income share of the pension?
What information do I need to provide about the duration of the pension?
Life annuities from taxed income depend on the lifetime of the beneficiary. If the annuity ends with the death of the beneficiary, it is important to indicate this in your tax return. The income share for private pensions is based on the age of the beneficiary at the start of the pension.
Fixed-term annuities from taxed income are also linked to a person's life but are limited to a specific term. They are paid until the end of the specified term at the latest but expire if the beneficiary dies earlier.
The term of the annuity is crucial for calculating the income share. Please note that pensions from the statutory pension insurance are not taxed based on the income share but with a higher taxation percentage.
Originally, people retiring from 2040 onwards were supposed to fully tax their statutory pension income. However, this has changed, as the taxation percentage will only increase by half a percentage point annually from 2023, starting with the 2023 pensioner cohort, and will reach 100 per cent for the first time in 2058 for that cohort (§ 22 No. 1 a) aa) EStG, amended by the "Growth Opportunities Act").
(2024): What information do I need to provide about the duration of the pension?
What is a capital gain pension?
A capital gain annuity occurs when, instead of receiving a one-off payment from the buyer for the transfer of your assets (e.g. business, property, land), you receive an annuity.
Important
There are special considerations for capital gain annuities from the sale of a business, agricultural enterprise, or professional practice. We recommend consulting a tax advisor in this case.
Capital gain annuities should be distinguished from pension annuities or recurring burdens and pure maintenance payments.
(2024): What is a capital gain pension?
What is a pension benefit?
A pension payment is made when a pension is paid to you by a legally entitled heir (e.g. spouse, children, parents).
In return, the pension recipient transfers certain assets to the pension payer.
Capital gains pensions must be distinguished from pension payments or long-term financial obligations and pure maintenance payments.
(2024): What is a pension benefit?
How are pension back payments taxed?
If you receive a pension back payment over a period longer than twelve months, this counts as remuneration for work over several years and is considered extraordinary income. This income can be taxed more favourably using the so-called one-fifth rule.
In this process, the eligible income is deducted from the taxable income, and then one fifth of it is added back. The income tax for the taxable income is then calculated, once with and once without the one-fifth amount. The difference is multiplied by five. This results in the tax for the extraordinary income.
The tax office automatically checks which calculation is more favourable for you. For the correct calculation, you must enter your received back payment separately. Enter any work-related expenses incurred in connection with the back payment (such as court or legal fees) separately as well.
Note: The Münster tax court ruled on 19 September 2019 (Ref. 5 K 371/19 E) that the reduced tax rate under § 34 EStG does not apply to a pension back payment relating to two assessment periods if the back payment is made in the second assessment period.
(2024): How are pension back payments taxed?
Sichern Sie sich einfach die volle Steuererstattung, die Ihnen zusteht!
Nur Lohnsteuer kompakt bietet Ihnen:
- Persönliche Steuertipps im Wert von 312 Euro (Durchschnitt)
- Verständliche Eingabehilfen und Erklärungen
- Import aus jeder beliebigen anderen Steuersoftware
- Schnelle Antworten bei Fragen
Jetzt kostenlos testen




